Power cable monitoring solutions
HVDC and HVAC underground power cables
HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) and HVAC (High Voltage Alternating Current) underground power cables are essential equipment used for power transmission and distribution systems, widely applied in energy transmission and distribution systems. These cables are typically buried underground and connect different power plants, substations, and electrical facilities.
The reliable operation of underground power cables is crucial for the stable power supply of the electrical system. However, the complexity of the underground environment and the challenges associated with long-term cable operation make cable monitoring a key task. Traditional monitoring methods often struggle to obtain timely and accurate cable condition information, necessitating a more advanced and reliable monitoring solution.

Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS) technology has emerged as an effective solution for monitoring HVDC/HVAC underground power cables. This technology utilizes fiber optic sensors installed along the cables to monitor the temperature changes in real-time and continuously. By measuring the variations in the optical properties of the fiber, it is possible to infer the temperature distribution of the cables and promptly identify potential issues.
The application of distributed fiber optic monitoring technology in HVDC/HVAC underground power cables enables real-time monitoring of cable temperature and detection of anomalies, thereby enhancing the reliability and safety of the power system.

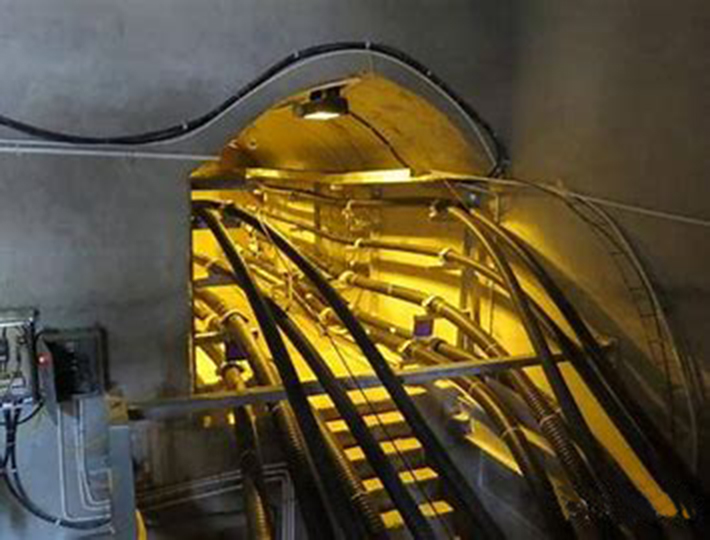
Fiber Optic Installation: Fiber optic sensors are installed at key positions and sections of underground power cables. The fiber can cover the entire length of the cables to enable continuous monitoring of temperature and strain. The fiber can be securely fixed to the surface or inside the cables using various installation methods.
Temperature and Strain Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of temperature and strain variations in the power cables is performed using fiber optic sensors. These sensors can measure the temperature and strain on the surface or inside the cables, providing accurate real-time data. This data helps in understanding the cable's operational status, load conditions, and potential issues.
Hotspot Detection: Distributed fiber optic temperature sensing systems can identify temperature hotspots within the cables, which are areas with abnormally high temperatures. These hotspots may indicate cable faults, load overload, or other problems. Prompt detection and management of these hotspots can prevent cable failures and accidents.
Warning and Alarm System: The distributed fiber optic temperature sensing system can be equipped with warning and alarm functionalities based on predefined temperature and strain thresholds. When the temperature or strain exceeds the set thresholds, the system triggers warnings and alarms, notifying operators to take appropriate measures to ensure the safe operation of the cables.

Data Collection and Analysis: The temperature and strain data collected by the fiber optic sensors are transmitted to the data acquisition system and processed and analyzed using analysis software. Through data analysis, the operational status of the cables, load characteristics, and potential issues can be understood, enabling the development of appropriate maintenance and management strategies.
Remote Monitoring and Control: The distributed fiber optic temperature sensing system can be connected to a remote monitoring platform, enabling remote monitoring and control. Operators can access monitoring data remotely, gaining real-time insights into the temperature and strain status of the cables and taking necessary measures to ensure the stable operation of the power system.
The distributed fiber optic monitoring technology for HVDC/HVAC underground power cables provides real-time temperature and strain monitoring capabilities, enhancing the reliability and safety of power transmission. This solution is widely applied in the field of power transmission, particularly for long-distance high-voltage transmission and under challenging environmental conditions, significantly contributing to the prevention of cable failures, optimization of operations, and improvement of system reliability.