Lord John William Rayleigh

Rayleigh(1842-1919)
Lord John William Rayleigh, a British physicist, made indelible contributions to the fields of acoustics, wave theory, optics, light scattering, electromagnetism, hydrodynamics, and fluid flow theory. In 1904, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of the inert gas argon (Ar).Rayleigh scattering refers to the scattering phenomenon produced by particles with sizes much smaller than the wavelength of the incident light. The scattering ability is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength. In Rayleigh scattering, the scattered light has the same wavelength as the incident light and does not undergo frequency changes (no energy change, same wavelength). It is a type of elastic light scattering.
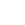
Rayleigh scattering in optical fibers: It is a fundamental loss mechanism caused by random fluctuations in the refractive index due to density variations during the manufacturing process of the fiber. This leads to local fluctuations in the refractive index, causing light to scatter in various directions.